All environment variables in PowerShell are stored in PS Drive under the Env: path. You can see that by running the following command:
|
1 |
Get-PSDrive |
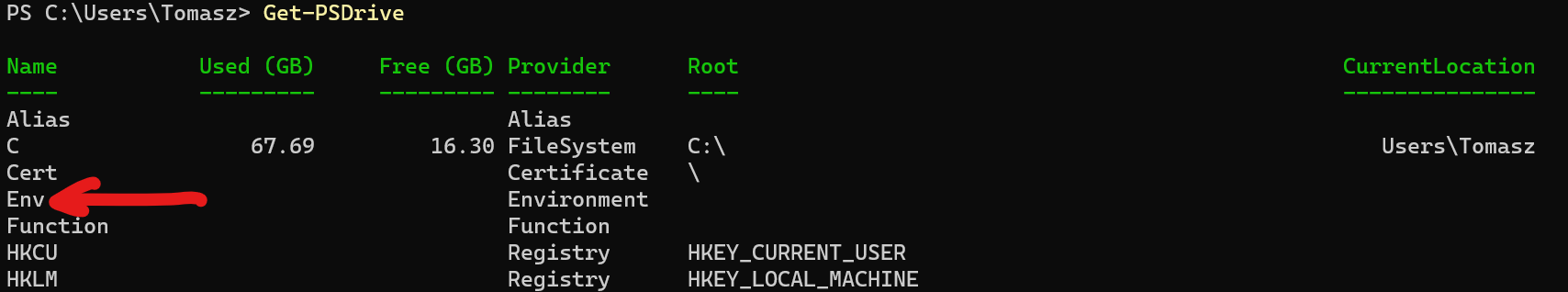
Here are three different methods you can use to get the Environment variables from “Env:”
- Method 1: Using the Get-ChildItem cmdlet or its aliases,
- Method 2: Using the System.Environment class in .NET framework,
- Method 3: Using the “$Env:VARIABLE_NAME” command.
Within Method 1, we will also see how to use regular expressions to match specific environment variables, sort the list of environment variables and send it to a file.
Method 1: Using the Get-ChildItem Cmdlet or its Aliases
You can get the list of all environment variables by running the following command in PowerShell:
|
1 |
Get-ChildItem Env: |
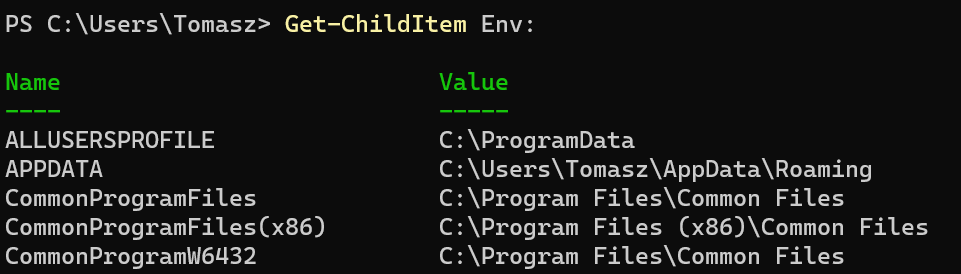
And if you want to get a value of a specific environment variable, use the command “Get-ChildItem Env:VARIABLE_NAME”, For example.
|
1 |
Get-ChildItem Env:APPDATA |
You can also use wildcards to match specific environment variables. In the example below, we retrieve all environment variables starting with “Program”.
|
1 |
Get-ChildItem Env:Program* |
The Get-ChildItem cmdlet has three aliases: dir, ls, and gc. You can see that by calling the Get-Alias cmdlet, as shown below.
Get-Alias -Definition Get-ChildItem 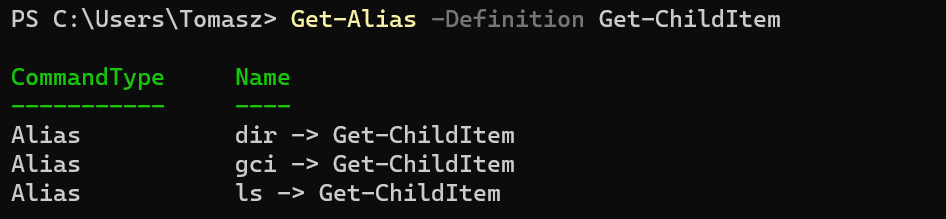
You can use any of them to retrieve environment variables in a similar manager, as shown below
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
# Retrieves all environment variables dir Env: # Get a specific variable ls Env:APPDATA # List all environment variables starting with "Program". gc Env:Program* |
Sorting the environment variables list and sending it to a file
The following command sorts the list by Name and then sends the result to a text file using the Out-File cmdlet. Note that you can also sort by Value.
|
1 |
Get-ChildItem Env: | Sort-Object Name |Out-File "variable.txt" |
Matching with regular expressions
Using wildcards to match patterns may be limiting. For that reason, you can use the -match operator to match regex patterns. For example
|
1 2 3 4 |
# Match environment variables starting with Program Get-ChildItem Env: | Where-Object {$_.Name -match "^Program"} # Fetches the environment variables whose values begin with "C:" and end with "Files". Get-ChildItem Env: | Where-Object {$_.Value -match "^C:.*Files$"} |
You can read more about regular expressions in PowerShell from these links: Regular Expression – Quick Reference and about_Regular_Expressions
Method 2: Using System.Environment Class
The System.Environment class in the .NET framework contains a static method called GetEnvironmentVariables() that retrieves all environment variables and their values. You can use the method to get a list of all environment variables by running the following command:
[System.Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariables()
Or get a specific environment variable using this command
|
1 |
[System.Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable("VARIABLE_NAME") |
Method 3: Using “$Env:VARIABLE_NAME” Command
The $Env variable is a built-in variable that provides access to all environment variables in the system. This variable can be queried to retrieve a specific environment variable using the command “$Env:VARIABLE_NAME”. For example
$Env:APPDATA
Conclusion
This post discussed three methods for getting a list of environment variables in PowerShell. The first method uses Get-ChildItem to list the contents of the Env: path (a path that hosts the environment variables). The second and third method uses System.Environment class and $Env variable, respectively.
In most cases, using the Get-ChildItem cmdlet discussed in Method 1 is sufficient. That is why, in that method, we discussed more – including how to sort the environment variable list, use regular expressions to match results, and send the output to a file.