Last time I wrote an article on how to write a list to a file. This time we are going the other way around: How to read data from a file and write it to a list.
The simplest way to append a file to a list is by using the following code:
|
1 2 |
with open('my_file.txt', 'r') as f: my_names = f.readlines() |
Let’s see how it works with the following text file.
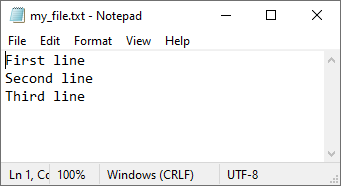
Let’s print it:
['First line\n', 'Second line\n', 'Third line']
The first two elements end with the newline character (\n).
Let’s use the for loop:
|
1 2 |
for name in my_names: print(name) |
This is what the result looks like:
First line Second line Third line
They are separated by the newline character. If you want to get rid of it, you can use the strip function.
|
1 2 3 |
with open('C:/my_file.txt', 'r') as f: my_names = [line.strip() for line in f] |
Now, there are no newline characters at the end of the file.
First line Second line Third line
Append CSV file to a list
If you are using a CSV file, instead of a text file, the code will be slightly more complicated.
This is the CSV file opened in a text editor:
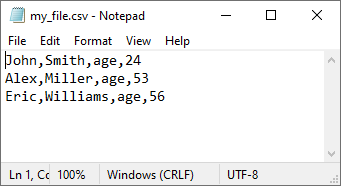
If you try to use the previous code, you are going to get the following result:
['John,Smith,age,24', 'Alex,Miller,age,53', 'Eric,Williams,age,56']
If that’s what you want, then ok, but you may want to create a list of lists.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
my_people = [] with open('C:/my_file.csv', 'r') as f: my_elements = [line.strip() for line in f] for element in my_elements: elements = element.split(',') my_people.append(elements) for person in my_people: print(person) |
Now, you have a beautiful list of lists:
['John', 'Smith', 'age', '24'] ['Alex', 'Miller', 'age', '53'] ['Eric', 'Williams', 'age', '56']