You can see this topic in two ways – determining the number of elements in a NumPy array or getting the memory size of the array. Let’s discuss this two.
Finding the Number of Elements in a NumPy Array
We will discuss three methods in this Section. Your array’s dimension and the used case will determine your chosen method.
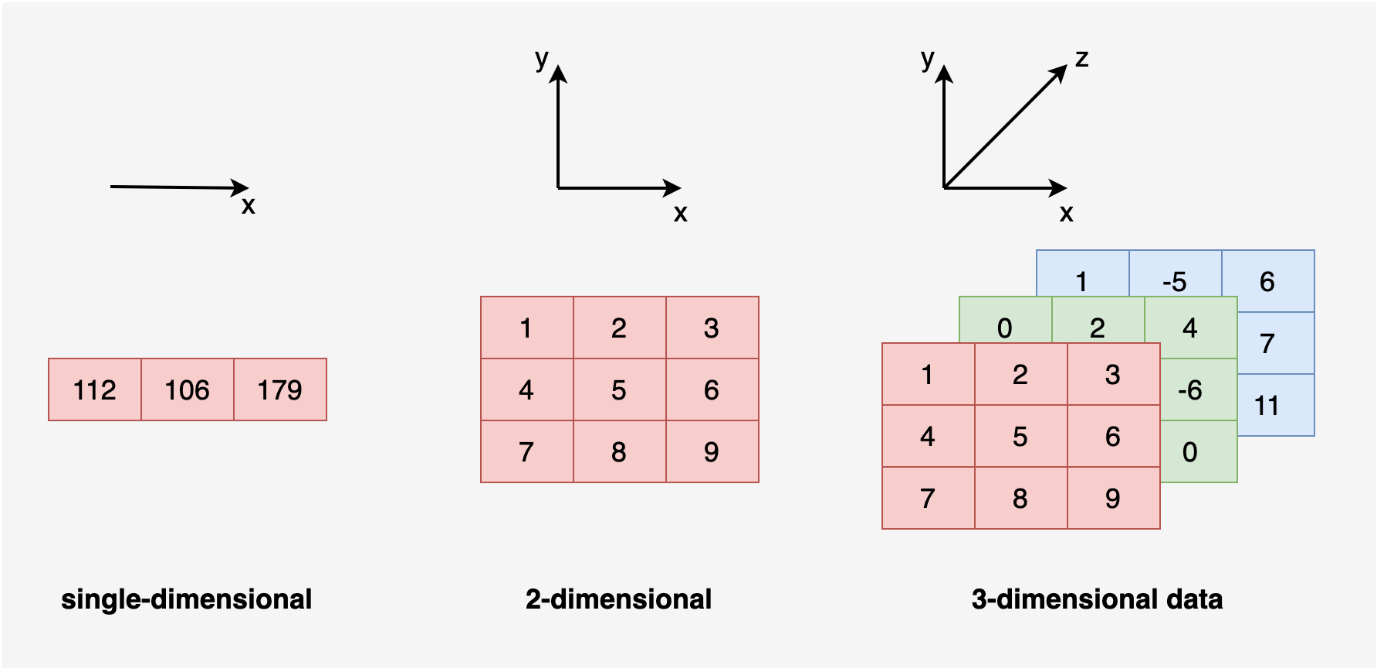
The dimensionality of data is the number of attributes a dataset has. The following Figure shows 1, 2, and 3-dimensional arrays.
Method 1: Using array.shape function
This function shows the number of elements along each dimension of the array. Here are some examples,
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
import numpy as np # Shape of a two-dimensional NumPy array arr1 = np.array([[14, 5, 17], [16, 2, 28], [ 4, 8, 15], [12, 10, 0]]) print(arr1.shape) # or np.shape(arr1) # Shape of a three-dimensional array arr2 = np.array([[[ 0, 21, 25, 7], [ 5, 8, 0, 0]], [[15, 16, 23, 9], [ 9, 2, 28, 0]], [[17, 3, 15, 4], [ 1, 0, 2, 8]]]) print(np.shape(arr2)) # or arr2.shape |
Output:
(4, 3) (3, 2, 4)
As shown in the output, arr1 has the shape of (4, 3) – 4 elements along the first dimension and 3 on the second.
Method 2: Using the len() function
This is the best method for finding the size of a 1-dimensional NumPy array.
If you are dealing with a multi-dimensional array, len() only shows the number of elements along the first dimension. For example,
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
import numpy as np # 1-dimensional NumPypy array arr1 = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]) print(len(arr1)) # 2-dimensional NumPy array arr2 = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [-1, -4, -5]]) print(len(arr2)) # 3-dimensional array arr3 = np.array([[[1, 2, 3], [1, 4, 7]], [[-1, 3, -6], [0, 4, 5]]]) print(len(arr3)) |
Output:
5 2 2
In multi-dimensional arrays, like arr2 and arr3, the function returns the size of the first dimension only.
Note: the output of len(array) is always equivalent to arr.shape[0].
Method 3: Using array.size NumPy attribute
This method returns the count of all elements in the array irrespective of the dimension of the array. For example,
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
import numpy as np # 1-dimensional numpy array arr1 = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]) print(arr1.size) # or np.size(arr1) # 2-dimensional numpy array arr2 = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [-1, -4, -5]]) print(np.size(arr2)) # or arr2.size # 3-dimensional array arr3 = np.array([[[1, 2, 3], [1, 4, 7]], [[-1, 3, -6], [0, 4, 5]]]) print(arr3.size) |
Output:
5 6 12
Method 4: Using np.shape() and np.prod() functions
As discussed in Method 1, the np.shape() function returns the size of each array dimension. If we want to get the actual number of elements in an array, we can simply multiply the values of np.shape() using the np.prod() function. Here are two examples.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
import numpy as np arr1 = np.array([16, 1, 23, 5, 1, 19, 23, 2, 28, 6]) print("Shape of arr1: ", np.prod(arr1.shape)) print("Size of arr1: ", np.prod(arr1.shape)) arr2 = np.array([[19, 21, 4, 6], [ 5, 8, 1, 24], [28, 10, 5, 3]]) print("Shape of arr2: ", arr2.shape) print("Number of elements in arr2: ", np.prod(arr2.shape)) |
Output:
Shape of arr1: 10 Size of arr1: 10 Shape of arr2: (3, 4) Number of elements in arr2: 12
Determining the Memory Size of a NumPy Array
This Section discusses two methods of determining the amount of memory a NumPy array takes.
Method 1: Using array.size and array.itemsize
This method takes the number of elements in an array and multiplies it with the amount of memory each item takes (derived by array.itemsize function) to get the total memory size taken by the array.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
import numpy as np # by default, it returns "int64" values arr1 = np.random.randint(1000, size=(16,16,17)) # size of a single array element print("Size of each int64 item: ", arr1.itemsize) # 8 bytes # multiply the memory size of single element with # the total number of items in the array. msize = arr1.itemsize*arr1.size #8*(16*16*17)=34816 print("Memory size of arr1: ", msize) # Generating unsigned int16 array arr2 = np.random.randint(1000, size=(16, 16, 17), dtype="uint16") # Each item of uint16 takes less memory than int64 on the example above print("Memory size of one uint16 item: ", arr2.itemsize) # 2 bytes total_size = arr2.itemsize*arr2.size print("Total memory size taken by arr2: ", total_size) |
Output:
Size of each int64 item: 4
The memory size of arr1: 17408
The memory size of one uint16 item: 2
Total memory size taken by arr2: 8704
Method 2: Using array.nbytes
This method outputs the amount of memory a NumPy array uses in bytes. For example,
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
import numpy as np arr1 = np.random.randint(1000, size=(16,16,17)) print("Memory size of arr1: ", arr1.nbytes) arr2 = np.random.randint(1000, size=(16, 16, 17), dtype="uint16") print("Memory taken by arr2: ", arr2.nbytes) |
Output:
Memory size of arr1: 34816 Memory taken by arr2: 8704
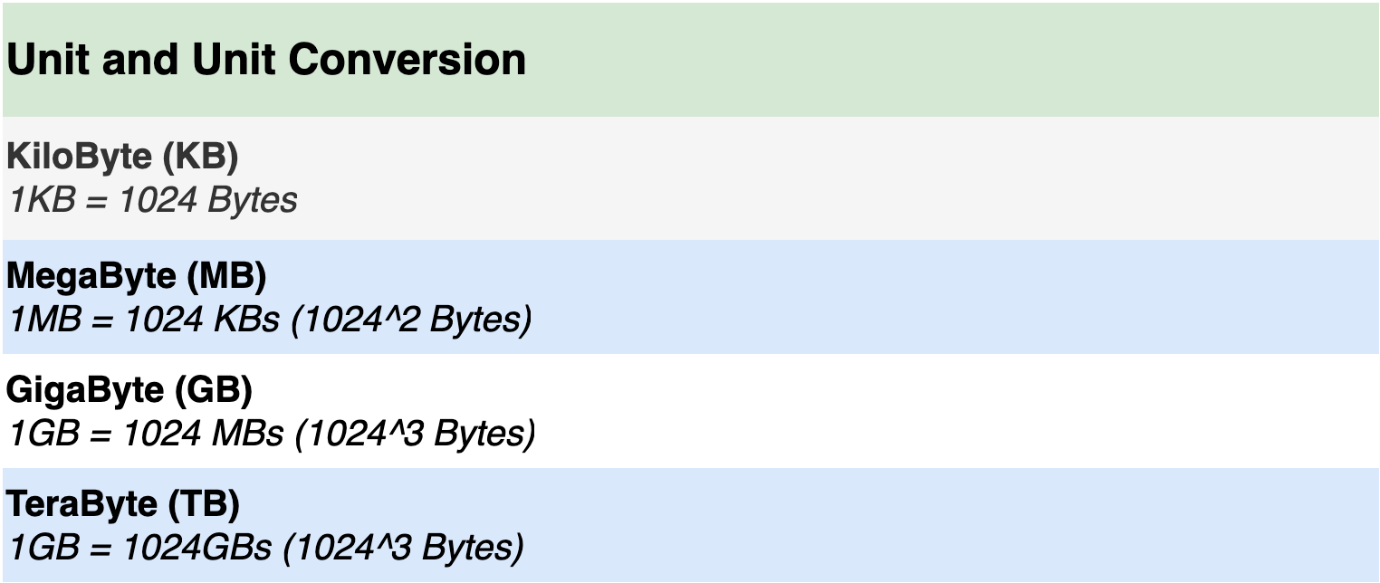
You can also use the following table to convert bytes into other memory units.
For example,
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
import numpy as np arr3 = np.random.randint(10000, size=(100, 100, 100), dtype="int64") print("Memory taken in bytes", arr3.nbytes) print("Memory taken in MBs", arr3.nbytes/(1024**2)) print("Memory taken in GBs", arr3.nbytes/(1024**3)) |
Output:
Memory taken in bytes 8000000 Memory taken in MBs 7.62939453125 Memory taken in GBs 0.007450580596923828
Conclusion
This guide discussed different methods for determining the size of a NumPy Array – size being the number of elements of the amount of memory it takes to store the array.